Energy Management
Energy Management is the process of monitoring, data collection, analysis, reporting, billing and energy consumption optimization.
There are 5 steps in the energy management process that need to be repeated over and over again:
- Collect data continuously
- Analyze and prepare reports from the obtained data
- Issuance of bills for subscribers and manage them
- Identify weaknesses and the need for maintenance or optimization of identified equipment
- Implement maintenance, optimization and development solutions
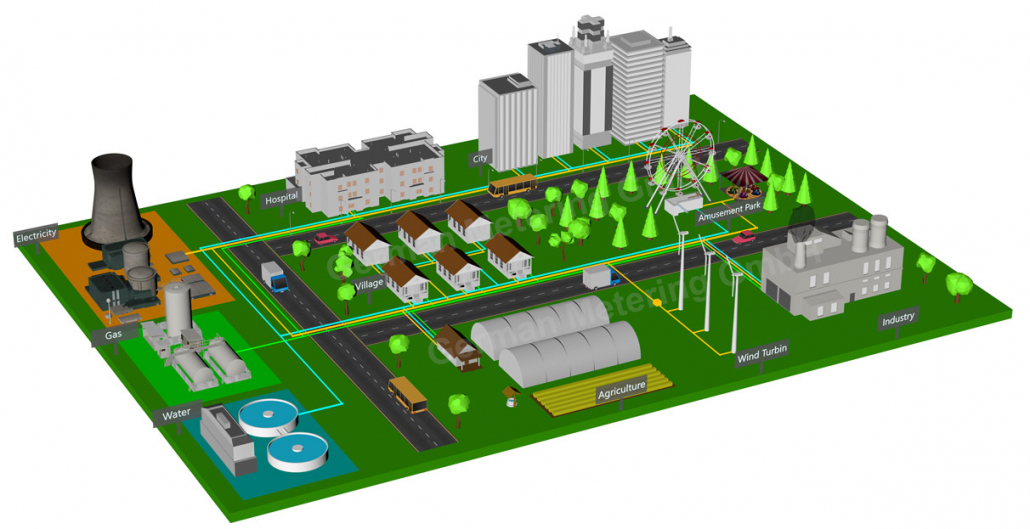
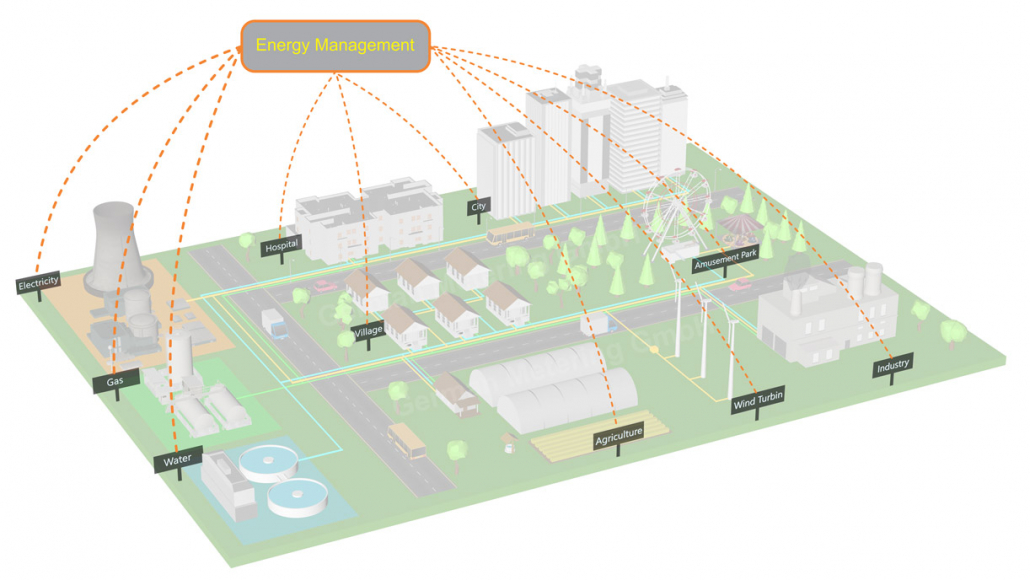
Energy management includes the planning and operation of energy production and consumption units, as well as energy distribution and storage. The goal is to protect natural resources, protect the climate and reduce greenhouse gases (GHG), while giving subscribers permanent access to the energy they need.
Another definition of energy management has been published which includes the economic dimensions: “Energy management is the proactive, organized and systematic coordination of energy supply, conversion, distribution and use to meet the requirements, taking into account environmental and economic goals”.
Energy Management Software (EMS)
One of the tools that helps a lot in the discussion of energy management, and without it, it would not be possible to manage energy in the way it is done today, is Energy Management Software or EMS. Today, with the help of this software and equipment that is installed in the desired location, everything can be monitored and controlled instantly.
Energy management software (EMS) refers to a group of energy-related software that may range from issuing and managing of customer’s water, electricity and gas bills, to instantaneous consumption measurement, monitoring and control of building HVAC systems, lighting control systems, building energy simulation and modeling, IT equipment management, energy auditing, etc.
Part of the features provided by energy management software is calculations related to energy consumption by subscribers, which finally, while controlling consumption and issuing bills for them, the possibility of categorizing subscribers according to their consumption (such as low-consumption subscribers, high-consumption subscribers, etc.) and for example, a warning can be sent to high-consumption consumers.
Energy management software can provide us with other features in order to control and reduce costs and energy consumption for buildings, industries, agriculture, etc. For this purpose, after collecting data, EMS uses it for three main purposes: monitoring, reporting, and action.
Monitoring includes process analysis and tracking of energy consumption to identify optimization opportunities. The report includes validation of data, benchmarking, and setting goals to reduce high-level energy consumption. Action also means instant control and responses (automatic or manual) to enhance energy conservation and display real-time energy consumption in web applications or energy dashboard.
Data Collection
Energy Management Software collects historic or real-time data. For example, these intervals can be from one minute to three months. This data is collected from intelligent meters, remote reading modems, sensors or other sources. In order to optimize energy consumption, previously collected data can be used with current data to compare energy consumption.
Data Analysis
Through the analysis of the collected data, with the help of the formulas provided by the Ministry of Energy, the bill issued to the subscribers and also the measures taken to save energy can be predicted and tracked. Analysis of energy production and consumption helps managers to make clearer decisions in order to maintain the energy production and distribution network, as well as future plans for its growth and development.
It is also possible to implement a system that analyzes energy consumption using intelligent algorithms that create a memory of energy use patterns and learn good and bad energy consumption behaviors and notify in case of abnormal energy use.
Reporting
Energy Management Software is more than just billing software. Its reports can be used to audit energy and even control greenhouse gas emissions (GHG). External factors affecting energy consumption, such as weather conditions, can be considered as part of the reporting process. This information can also be used to prioritize energy conservation and control plans and at higher levels to balance the cost of energy production and related capital.
Monitoring
Monitoring tools display real-time and historical data. Sometimes EMS includes a variety of benchmarking tools, such as energy consumption per square meter, climate normalization, or more advanced analysis using energy modeling algorithms to detect wastage or abnormal consumption. Accurate observation of energy usage time combined with abnormal consumption detection can show managers optimization opportunities.
The replacement of worn or inefficient equipment, equipment optimization and removal of unnecessary loads can be done using EMS reports. For example, an unexpected increase in energy at a particular time each day may indicate improper adjustment or malfunction of equipment. Reports can also be used for energy monitoring and targeting.
When consumption values exceed predefined thresholds based on consumption or cost, the EMS may issue warnings via text messages or other methods. These thresholds may be set at absolute levels, or use an energy model to determine if consumption is abnormally high or low.
Action
Action can refer to automatic or manual responses to energy data collected and analyzed. Building control systems can easily respond to energy fluctuations, just as a heating system can respond to temperature changes. EMS can automate the shutdown process by increasing consumption.
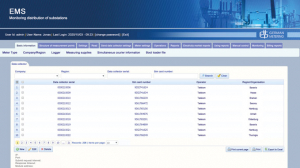
German Metering’s Product
In order to manage energy and to meet this important need in the field of energy, German Metering GmbH has produced products that meet the needs of energy producing and distributing organizations (in the field of electricity, water and gas). A number of our web applications:
- Meter Data Management
- Monitoring substations
- Water Meter Data Management
- Gas Meter Data Management