Meter Data Management (MDM)
Meter Data Management (MDM) is a software that performs long-term data storage and management for large amounts of data delivered by smart metering systems. This data mainly consists of subscriber consumption and events that are imported from servers that manage data sets in Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI) or Automatic Meter Reading (AMR) systems. MDM is a component of smart grid infrastructure provided by utility companies. MDM includes meter data analysis, the analysis of data collected from electric smart meters that record electrical energy consumption.
MDM Systems
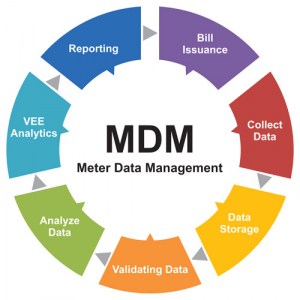
Meter Data Management (MDM) system usually validates, cleans and processes incoming data and then uses them for billing, analysis and reporting. MDM software can include:
- Planning and managing the expansion of smart meters
- Monitor and manage network meters and equipment
- Smart meter routines (adding, deleting, updating meter information and all kinds of requests)
- Bill issuance
In addition, MDM may provide reports for load and demand forecasting, management reports, and customer service metrics.
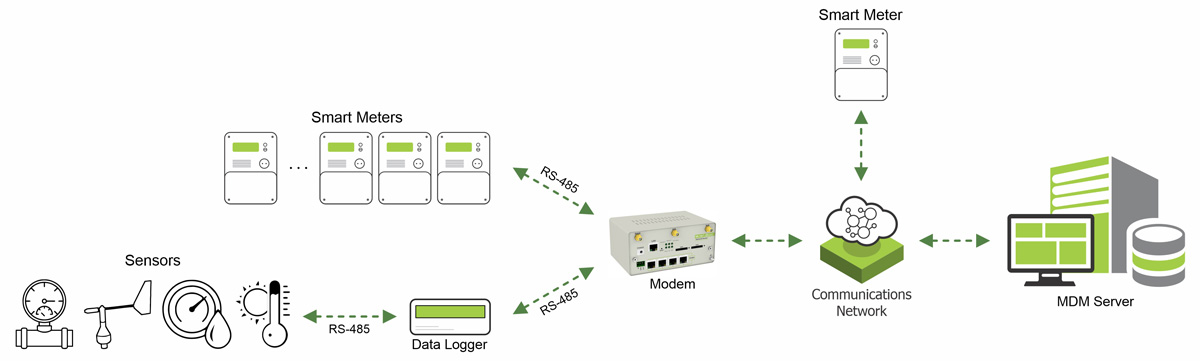
MDM provides application programming interfaces (APIs) between MDM and multiple destinations that rely on meter data. This is the first step to ensure that data consistency processes are in place. In addition to this common functionality, an advanced MDM may provide facilities for remote connect/disconnect of meters, verification of power status/restoration, and remote meter reading on demand.
Data Analysis
Smart meters send consumption data of subscribers (in residential, commercial and industrial uses) to central head end server systems at specified times. Utility companies collect and analyze this massive data. Some of the reasons why data should be analyzed are:
- Making efficient decisions for purchasing energy based on consumption patterns
- Setting up energy efficiency or energy discount programs
- Compare and correct the performance of the measurement service provider
- Identifying and reducing unbilled energy (such as energy waste, leaks, tampered meters, etc.)
This data not only helps utility companies make their businesses more efficient, but also helps consumers save money by using less energy during peak times. Therefore, it is both economical and green. Smart meter infrastructure is relatively new for the water and electricity industry. As utilities collect more data over the years, they may have more uses for these precise smart meter activities.
Benefits of Meter Data Management (MDM)
With a comprehensive Meter Data Management (MDM) strategy and the right way of working, these things can be achieved:
- Improve data efficiency
- More detailed information about shared consumption
- Improve insight and decision making
- Creating competitive advantage and efficiency
- Risk reduction and easy compliance with regulations
MDMS (Meter Data Management System)
Meter Data Management System (MDMS) provides application programming interfaces (APIs) between MDMS and multiple servers that rely on meter data. Its advantages:
- Save all meter readings in the registration system
- Confirmation of correct operation and accuracy of meter reading and events
- Evaluation of possible locations or problems that require a field visit
- Improve data estimation and validation using multidimensional analysis
- Data synchronization between MDMS, AMR/AMI databases
- Improve utility back-office operations
- Realize the investment potential in AMI
Future Vision
Metering has evolved from merely a part of the revenue cycle to an organizational function that supports several core business processes and delivers operational benefits. For utilities undergoing digital transformation, it is critical to have the right business solution to drive mission-critical operations and new customer-focused solution. The chosen solution should be more than a typical MDM platform that serves as the digital backbone for energy companies.
The solution should provide a vision of the future for its users, define new business models and use cases, and enable the integration of machine learning functions and other data analytics-based solutions.
Modern Technology, Modern Market
Utilities, in their Meter Data Management (MDM) evaluation process, should consider a workflow designed and built with the latest IT technologies used at hyperscale by social network applications. MDM must be designed for infinite scale, and with maximum flexibility in a rapidly changing utility sector.
Business Foundation
The capabilities of a chosen MDM solution should provide a foundation that enables the utility to:
- Integration of all information related to measurement management processes and systems in one place
- Providing the same mechanisms for the processing and measurement process
- Simplifying the process related to measurement management, taking advantage of platform capabilities that provide software infrastructure, services and data models for greater flexibility and speed in business and adaptability to regulatory changes.
- Creating opportunities and new business models using interactive and open platform capabilities with data analysis and machine learning technologies.
Main Requirements to Consider
- Reducing the number of applications and systems involved in measurement management processes.
- All required facilities in one platform, both Head-Ends and Client OT/IT systems, which follow the standards defined by the utility.
- Common end-to-end tracking and auditing mechanisms for all processes and applications managed by the platform.
- A single, common user-friendly interface for all applications, providing a homogenous, user-defined landscape.
- The energy supplier can fully focus on creating business value from the data for its customers.
- Unlike a custom-developed solution, maintenance throughout the operational lifetime of the system and automatic access to valuable new features are included in SaaS.
- Advanced data analysis and machine learning capabilities.