Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI)
Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI) refers to systems that measure, collect and analyze energy consumption and with measuring equipment such as electricity meters, gas meters and water meters, according to they communicate on request or on a scheduled basis. These systems include hardware, software, communications, common energy consumption displays and controllers, customer communication systems, meter data management software, and supplier business systems.
Government agencies and water, electricity and gas companies are turning to Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI) systems as part of a larger “Smart Grid” initiative. AMI extends Automated Meter Reading (AMR) technology by providing two-way meter communication, allowing commands to be sent to meters and other metering equipment for multiple purposes, including utility-based tariff information. on consumption hours, responding to requests, disconnecting and connecting energy remotely, etc.
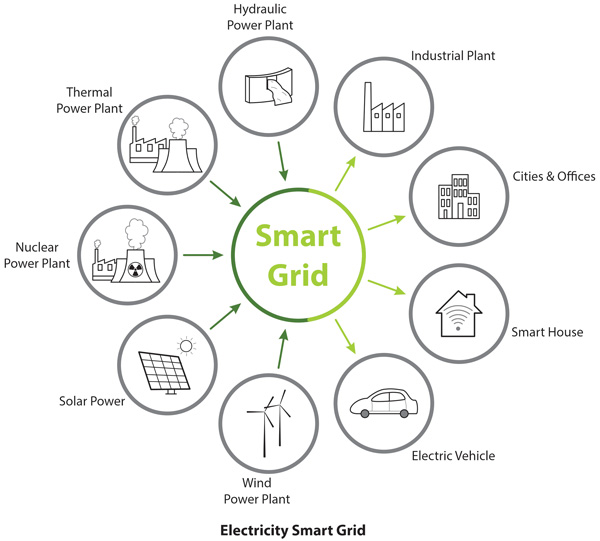
Wireless technologies are critical elements in the local area network, creating a network configuration of up to thousands of meters to send and receive information with the central server of the energy supply company.
The network established between the measuring equipment and the central server enables the collection and distribution of information to energy suppliers and subscribers. Subscribers can change their normal consumption patterns to lower their costs by using the information provided by the system. Tariffs can also be used to curb the increase in consumption during peak hours.
Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI) is an integrated system of equipment, communications and information management systems for energy providers to collect real-time customer consumption information remotely. AMI uses radio-based technology to read meters. uses that eliminates the need to read meters manually.
Meter data is sent to the supplying company through a fixed network. This company can use the data for maintenance, improving the stability and efficiency of the system by effectively monitoring energy consumption and identifying weak points.
How Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI) Works
The meters measure and store the energy consumed by the subscribers, their measuring method can be different according to their types and mechanisms. Data is transferred wirelessly through the GPRS platform or optical fiber through the Internet to the information management system.
Information can be transferred from other measuring equipment such as pressure sensor, temperature sensor, humidity sensor, vibration sensor, sound sensor, etc. to the information management system, and they can also be included in the SCADA system. The received data are analyzed on the server and useful reports can be prepared from them.
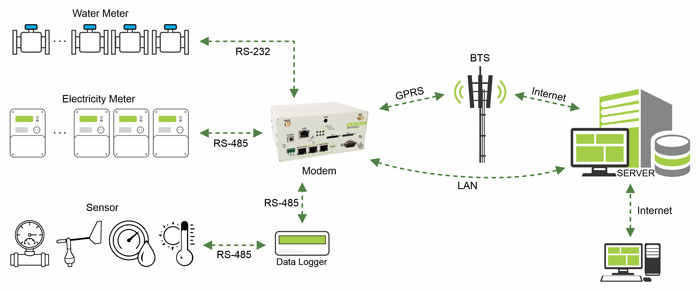
It is possible for energy suppliers to connect and disconnect the subscriber’s service remotely. This is possible for electricity suppliers through a relay, and for water and gas suppliers through a solenoid valve. If the subscriber tampers with the meter, an alarm will be sent to the server.
Benefits of Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI)
- Improved Utility Operations
- Improved Water Conservation
- Leaks Detection
- Enhanced Security
- System Resilience
AMI solutions are scalable, so energy suppliers may implement the system depending on their budget and needs. AMI fully automates the reading, meter data collection and billing processes, making it a long-term and sustainable business solution for companies.
AMI projects go through several stages:
- Initial Identification
- Feasibility Study
- Contract Negotiations
- Installation
- Executive Operations
- Maintenance
- Transformation of the Business Process
Automated Meter Reading (AMR)
Automatic Meter Reading (AMR) is a communication technology that energy companies use to automatically collect energy consumption and customer status data from meters. AMR system can be on foot or by car. In this system, the device is carried by the agent or placed inside a car. When it passes through the place, the meter information is received by radio waves and stored in the device. With this method, the agent no longer needs to see the meter, and the problem of closed or blocked subscribers is also solved.

After collection, the data from the meters is transferred to a database where the energy supply company can monitor and analyze the amount of consumption of the subscribers and troubleshoot the problems. Also, issue bills in a shorter period of time, based on collected consumption data.
AMI vs. AMR
Automatic Meter Reading (AMR) technology enables accurate and timely meter reading, which is accomplished by installing a radio-based module called an ERT module on a meter. Readings are collected by a meter reader using a handheld or vehicle-based radio device or by a fixed network system.
The AMR system means that meter readers no longer need to enter the customer’s home, however AMR is rapidly being replaced by AMI, as AMI improves system reliability and future operational efficiency. Compared to AMR, AMI allows for reduced manpower due to efficiency, so companies can focus their attention elsewhere.
AMI is different from automatic reading system (AMR) because unlike AMR which is one-way communication, AMI enables two-way communication with the meter. Systems that are only capable of meter reading are known as AMR systems.
In the comparison between AMR and AMI, the AMI system has the following advantages:
- No need to refer human resources
- Much higher speed of reading and collecting information
- Instant reading
- Receive information every time of the day and night
- Connecting and disconnecting subscriber service remotely
- Real-time notification of outages
- Real-time notification of meter manipulation
- Detection of possible leaks